Introduction
Phobias are intense and irrational fears of specific situations, objects, or activities. They can cause significant distress and interference with daily life. If left untreated, phobias can worsen over time and lead to other anxiety disorders. However, with the right approach, it is possible to treat and manage different types of phobias effectively. This article aims to explore various treatment methods and strategies for overcoming different phobias.
Table of Contents:
check my blog –Attention Deficit Disorder and Benefits of Psychotherapy
Definition of Phobia
A phobia is an overwhelming fear of something that poses little or no real danger. This fear is often disproportionate to the actual threat posed by the situation or object. Phobias can lead to avoidance behaviours and can be categorized into different types based on the triggering stimuli.
Common Types of Phobias
- Specific Phobias: These phobias involve fear of specific objects or situations, such as heights, spiders, or flying.
- Social Phobia: Also known as social anxiety disorder, it involves fear and anxiety in social situations.
- Agoraphobia: This is a fear of being in situations where escape might be difficult or embarrassing.
- Claustrophobia: It is the fear of enclosed spaces.
- Glossophobia: This phobia is characterized by a fear of public speaking.
- Atychiphobia: It involves an extreme fear of failure or making mistakes.
- Nyctophobia: This is the fear of the dark.
- Zoophobia: It is a fear of animals.
- Trypanophobia: This phobia involves fear of medical procedures like injections or needles.
- Aquaphobia: It is the fear of water.
- Astraphobia: This phobia is characterized by fear of thunder and lightning.
Causes of Phobias
Phobias can develop due to various factors, including genetic predisposition, traumatic experiences, learned behaviours, and cultural influences. Understanding the root cause of a phobia is crucial in determining the most effective treatment approach.
Treatment of Phobias
1. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized and evidence-based psychotherapy approach used to treat various mental health conditions, including phobias. It aims to identify and modify negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to the development and maintenance of anxiety and phobic responses.
How CBT Works:
a. Identification of Negative Thoughts: In the initial stages of CBT, the therapist works with the individual to identify negative thoughts and beliefs associated with the phobia. These thoughts are often irrational and exaggerated, contributing to anxiety and fear.
b. Challenging Cognitive Distortions: Once the negative thoughts are identified, the therapist helps the individual challenge and reframe them. They encourage the person to examine the evidence supporting or refuting these thoughts, leading to a more balanced perspective.
c. Behavioral Exposure: Exposure is a crucial component of CBT for phobias. The therapist gradually exposes the individual to the feared object or situation in a controlled and safe manner. This exposure helps desensitize the individual to the fear triggers over time.
d. Coping Strategies: Individuals are taught coping skills to manage anxiety and fear when confronted with the phobic trigger. Breathing exercises, relaxation techniques, and visualization are commonly taught to help individuals stay calm during exposure.
e. Homework Assignments: Between therapy sessions, individuals are often given homework assignments to practice what they’ve learned and apply coping techniques in real-life situations.
2. Exposure Therapy: Effective Treatment of Phobias
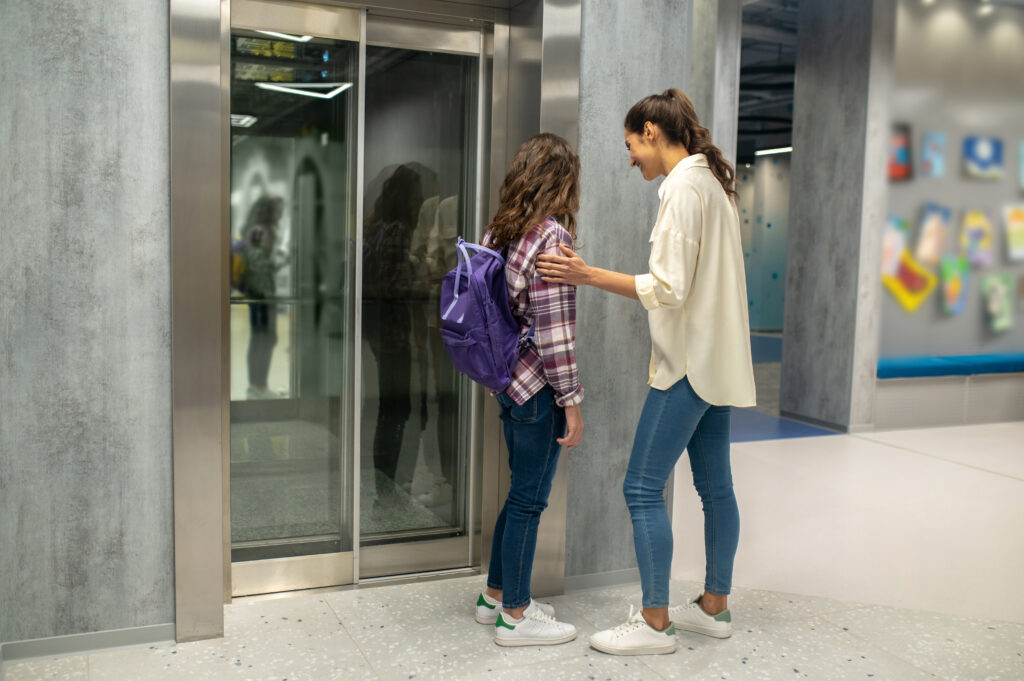

Image by zinkevych on Freepik
Exposure therapy is a specialized form of cognitive-behavioral therapy primarily focused on systematically exposing individuals to their phobic triggers. This is very useful technique foe the treatment of Phobias.The goal is to reduce the emotional response to the feared object or situation by gradually increasing exposure levels.
How Exposure Therapy Works:
a. Creating a Fear Hierarchy: The therapist works with the individual to create a fear hierarchy, a ranked list of feared situations or objects from least to most anxiety-provoking.
b. Gradual Exposure: Starting from the least feared item on the hierarchy, the individual is exposed to the phobic trigger in a controlled and safe environment. As the person becomes more comfortable with each step, they progress to the next item on the hierarchy.
c. Desensitization: With repeated exposure, the individual’s anxiety response gradually diminishes. This process is called desensitization, as the person becomes less sensitive to the phobic trigger.
d. Imaginal Exposure: In some cases, when direct exposure is not feasible, imaginal exposure is used. The individual is guided to vividly imagine the feared situation, which can also lead to desensitization.
3. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques:

Mindfulness and relaxation techniques are valuable tools for managing anxiety and stress associated with phobias. They help individuals stay present in the moment and reduce overwhelming thoughts and fears. It is one of the effective Treatment of Phobias.
How Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques Work:
a. Mindfulness Meditation: Mindfulness involves paying non-judgmental attention to the present moment. Through regular mindfulness meditation, individuals learn to observe their thoughts and feelings without reacting to them emotionally. This can help in reducing anxiety and increasing emotional resilience.
b. Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR): PMR is a technique that involves tensing and relaxing different muscle groups systematically. This helps release physical tension and promotes relaxation.
c. Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing exercises, also known as diaphragmatic breathing, can help individuals activate their body’s relaxation response and reduce anxiety.
4. Support Groups:
Joining a support group for individuals with similar phobias can provide valuable emotional support and encouragement during the treatment of Phobias.
How Support Groups Work:
a. Shared Experiences: In a support group, individuals can share their experiences, fears, and progress with others who understand what they are going through. This sense of camaraderie can be comforting and empowering.
b. Peer Support: Members of the support group can offer practical tips and coping strategies they have found helpful in managing their own phobias.
c. Motivation and Encouragement: Being part of a support group can provide motivation to stay committed to treatment and overcome challenges along the way.
5. Biofeedback Therapy:
Biofeedback therapy is a technique that uses monitoring devices to provide individuals with real-time information about their physiological responses to fear and is a good technique as Treatment of Phobias.
How Biofeedback Therapy Works:
a. Physiological Monitoring: During a biofeedback session, sensors are attached to the individual’s body to measure physiological responses such as heart rate, muscle tension, and skin conductance.
b. Feedback and Awareness: The individual receives immediate feedback on their physiological responses through visual or auditory cues. This helps them become more aware of their body’s reactions to fear.
c. Self-Regulation: With the help of a therapist, individuals learn relaxation and self-regulation techniques to control their physiological responses. Over time, they can gain more control over their anxiety reactions.
6. Virtual Reality Therapy:
Virtual Reality (VR) therapy is an innovative approach used to expose individuals to their phobic triggers in a controlled and immersive virtual environment.
How Virtual Reality Therapy Works:
a. Realistic Simulations: Virtual reality technology creates realistic simulations of the feared situation, object, or environment.
b. Gradual Exposure: Individuals are gradually exposed to the phobic trigger within the virtual environment. The therapist can customize the exposure intensity based on the individual’s comfort level.
c. Safe Environment: VR therapy provides a safe and controlled setting for exposure, allowing individuals to face their fears without real-world consequences.
d. Therapist Guidance: Throughout the session, a trained therapist guides and supports the individual, helping them manage anxiety and navigate the virtual experience.
7. Self-Help Techniques:
In addition to professional therapy, individuals can also adopt self-help techniques to manage and overcome their phobias. These techniques empower individuals to take an active role in their treatment journey. This is very useful technique for the Treatment of Phobias.
Common Self-Help Techniques:
a. Education and Awareness: Understanding the nature of phobias, their triggers, and the impact they have on one’s life is the first step to conquering them. Educating oneself about the specific phobia can demystify the fear and provide a sense of control.
b. Facing Fears Gradually: Gradual exposure to the feared object or situation is a self-help approach inspired by exposure therapy. Individuals can create their own hierarchy and start confronting their fears one step at a time.
c. Positive Affirmations: Using positive affirmations and self-encouragement can help challenge negative thoughts related to the phobia. Repeating positive statements can instill confidence and courage.
d. Journaling: Keeping a journal to record thoughts, emotions, and progress can help individuals track their journey and identify patterns or triggers related to their phobia.
e. Visualization: Imagining successful and anxiety-free encounters with the phobic trigger can help individuals build confidence and reduce fear responses.
8. Hypnotherapy:

Image by storyset on Freepik
Hypnotherapy, also known as hypnosis, is an alternative therapy that uses relaxation and focused attention to create a heightened state of suggestibility. It can be beneficial for individuals seeking an alternative approach to address phobias.
How Hypnotherapy Works:
a. Deep Relaxation: The hypnotherapist guides the individual into a state of deep relaxation, called trance, where the mind becomes more open to suggestions.
b. Exploring Root Causes: During hypnosis, the therapist may help the individual explore any underlying causes or subconscious associations related to the phobia.
c. Reframing Thoughts: The therapist can use positive suggestions to reframe negative thought patterns and beliefs surrounding the phobia.
d. Empowerment: Hypnotherapy aims to empower individuals to develop a sense of control over their phobia and build confidence in their ability to manage fear responses.
9. Play Therapy (For Childhood Phobias):
Play therapy is a specialized form of therapy used to help children express and process their emotions, including those related to phobias.
How Play Therapy Works:
a. Child-Centered Approach: Play therapy is child-centered, allowing the child to lead the play session and express themselves in a non-threatening manner.
b. Use of Play Materials: The therapist provides a variety of play materials, such as toys, art supplies, and puppets, to allow the child to explore and communicate their feelings.
c. Therapeutic Expression: Through play, children can act out their fears and anxieties, allowing the therapist to gain insights into the root causes of the phobia.
d. Skill-Building: Play therapy can teach coping skills, emotional regulation, and ways to manage anxiety, enabling the child to confront and cope with their phobia.
10. Behavioral Techniques: Treatment of Phobias
Behavioral techniques involve changing specific behaviors associated with the phobia to reduce fear responses and increase adaptive coping.
Common Behavioral Techniques:
a. Systematic Desensitization: Similar to exposure therapy, systematic desensitization involves gradual exposure to the phobic trigger while pairing it with relaxation techniques.
b. Response Prevention: This technique involves preventing the individual from engaging in avoidance behaviors or rituals related to the phobia. By breaking the cycle of avoidance, anxiety is reduced over time.
c. Positive Reinforcement: Rewarding positive behaviors and efforts in facing the phobia can motivate individuals to continue their progress.
d. Modeling: Observing others successfully confront and manage the phobia can provide inspiration and increase self-efficacy.
Case Studies:
To better understand the effectiveness of non-medication treatment for phobias, let’s explore two hypothetical case studies:
Case Study 1: Social Phobia
John, a 30-year-old marketing professional, struggles with social phobia. He experiences intense anxiety in social settings and avoids social gatherings, networking events, and public speaking opportunities. Through cognitive-behavioral therapy, John learns to challenge his negative thoughts and fears related to social interactions. With the help of his therapist, he gradually exposes himself to social situations, starting with small gatherings with close friends. Over time, John gains confidence and manages to attend larger social events. Through continuous practice, he successfully overcomes his fear of public speaking and takes up leadership roles at work.
Case Study 2: Specific Phobia (Fear of Flying)
Sarah, a 25-year-old travel enthusiast, has a specific phobia related to flying. Her fear prevents her from exploring new destinations and fulfilling her dream of traveling the world. With exposure therapy, Sarah begins by visualizing herself at an airport and gradually progresses to watching videos of flight take-offs and landings. As she gains comfort, Sarah visits an airport without boarding a flight. With time, she takes short domestic flights and eventually conquers her fear by flying on long-haul international flights. Sarah now embarks on adventures with confidence, knowing her phobia no longer holds her back.
Importance of Seeking Professional Help:
While self-help techniques can be valuable, seeking professional help is essential for a comprehensive and tailored approach to phobia treatment. Trained therapists can identify the root causes of phobias, guide individuals through exposure processes, and offer emotional support throughout the journey. They also ensure treatment strategies align with the individual’s specific needs and progress.
Treating Specific Phobias
Exposure Therapy
Exposure therapy is a common and effective treatment for specific phobias. It involves gradual and controlled exposure to the feared object or situation. The goal is to reduce anxiety and fear responses over time.
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT)
CBT is another widely used approach in treating phobias. It focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and beliefs associated with the phobia. By changing these thought patterns, individuals can learn to respond differently to the phobic triggers.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help manage the symptoms of phobias. Anti-anxiety medications and beta-blockers are commonly used to reduce anxiety and physical symptoms associated with phobias. However, medications are usually used in conjunction with therapy for better results.
Overcoming Social Phobias
Social Skills Training
Social skills training can be beneficial for individuals with social phobias. It involves learning and practicing social skills in a controlled and supportive environment.
Support Groups
Joining support groups can provide individuals with social phobias a safe space to share their experiences, learn from others, and receive encouragement.
Managing Specific Phobias
Fear of Heights (Acrophobia)
Individuals with acrophobia can benefit from exposure therapy, where they gradually face heights in a safe and controlled manner.
Fear of Spiders (Arachnophobia)
Exposure therapy combined with cognitive techniques can help individuals with arachnophobia manage their fear of spiders.
Fear of Flying (Aviophobia)
Cognitive techniques and relaxation exercises can aid in reducing the fear of flying in aviophobia sufferers.
Coping with Agoraphobia
Gradual Exposure
Gradual exposure to public spaces can help individuals with agoraphobia build confidence and reduce anxiety.
Breathing Techniques
Learning deep breathing techniques can be helpful in managing anxiety and panic attacks associated with agoraphobia.
Handling Claustrophobia
Desensitization
Desensitization involves gradually exposing individuals with claustrophobia to enclosed spaces, allowing them to become more comfortable over time.
Relaxation Techniques
Practicing relaxation techniques can help individuals manage anxiety and fear when faced with claustrophobic situations.
Conquering Fear of Public Speaking (Glossophobia)
Practice and Rehearsal
Regular practice and rehearsal can boost confidence and reduce anxiety for individuals with glossophobia.
Visualization Techniques
Visualization can help in mentally rehearsing successful public speaking experiences.
Treating Fear of Failure (Atychiphobia)
Setting Realistic Goals
Learning to set achievable goals can help individuals with atychiphobia overcome their fear of failure.
Positive Self-talk
Replacing negative self-talk with positive affirmations can build self-confidence and combat atychiphobia.
Coping with Fear of the Dark (Nyctophobia)
Nightlight and Comfort Objects
Using nightlights and comfort objects can provide a sense of security for those with nyctophobia.
Sleep Routine
Establishing a consistent and calming sleep routine can ease anxiety associated with nyctophobia.
Dealing with Fear of Animals (Zoophobia)
Gradual Exposure
Gradual exposure to animals in a controlled setting can help individuals with zoophobia become more comfortable.
Pet Therapy
Pet therapy, involving interactions with animals in a therapeutic environment, can be beneficial for zoophobia sufferers.
Managing Fear of Medical Procedures (Trypanophobia)
Communication with Medical Professionals
Open communication with medical professionals can help individuals with trypanophobia express their fears and receive appropriate support.
Relaxation Techniques
Learning relaxation techniques can help manage anxiety during medical procedures.
Overcoming Fear of Water (Aquaphobia)
Swimming Lessons
Learning to swim can be an empowering experience for individuals with aquaphobia.
Desensitization
Gradual exposure to water can help reduce fear and anxiety in aquaphobia sufferers.
Handling Fear of Thunder and Lightning (Astraphobia)
Safety Measures
Implementing safety measures during storms can help individuals with astraphobia feel more secure.
Distraction Techniques
Engaging in distracting activities during thunderstorms can help take focus away from the fear.
Overcoming Fear of Medical Procedures (Trypanophobia)
Communication with Medical Professionals
Open communication with medical professionals can help individuals with trypanophobia express their fears and receive appropriate support. Medical staff can provide information about the procedure, answer questions, and offer reassurance, which can significantly reduce anxiety.
Relaxation Techniques
Learning relaxation techniques can help manage anxiety during medical procedures. Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery are some effective relaxation techniques that individuals can practice before and during medical interventions.
Overcoming Fear of Water (Aquaphobia)
Swimming Lessons
Learning to swim can be an empowering experience for individuals with aquaphobia. Taking swimming lessons with a patient and supportive instructor can gradually build confidence and comfort in the water.
Desensitization
Gradual exposure to water can help reduce fear and anxiety in aquaphobia sufferers. Starting with small steps, such as splashing water on the face or feet, and gradually progressing to wading in shallow water, can help individuals become more accustomed to being in water.
Handling Fear of Thunder and Lightning (Astraphobia)
Safety Measures
Implementing safety measures during storms can help individuals with astraphobia feel more secure. Installing lightning rods or surge protectors in the home, staying away from windows during storms, and creating a designated safe space can provide a sense of protection.
Distraction Techniques
Engaging in distracting activities during thunderstorms can help take focus away from the fear. Listening to calming music, watching a favorite movie, or doing a relaxing hobby can help divert attention from the storm-related anxiety.
Conclusion
Phobias are common but treatable anxiety disorders that can significantly impact an individual’s life. Recognizing the specific type of phobia and seeking professional help are crucial steps toward effective treatment. Exposure therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and social support are valuable tools in overcoming different types of phobias. Moreover, combining these approaches with relaxation techniques and positive thinking can lead to positive outcomes.
If you or someone you know struggles with phobias, remember that help is available, and seeking support from mental health professionals is essential in developing a personalized treatment plan. By addressing phobias with compassion and patience, individuals can take significant steps toward reclaiming their lives and experiencing a newfound sense of freedom.
FAQs
- Q: Can phobias develop in adulthood?
- A: Yes, phobias can develop at any age, even in adulthood, due to various life experiences.
- Q: How long does it take to treat a phobia?
- A: The duration of treatment varies for each individual and depends on the severity of the phobia and the chosen treatment method.
- Q: Are all phobias irrational?
- A: Yes, phobias are considered irrational because the fear is disproportionate to the actual threat.
- Q: Can phobias run in families?
- A: Yes, there is evidence to suggest that phobias may have a genetic component and can run in families.
- Q: Is medication the only treatment for phobias?
- A: No, medication is just one of the treatment options, and it is often used in combination with therapy for better results.
Check my related links:
Website-http://www.positiveworldcounselling.com
Instagram- https://www.instagram.com/positiveworld2632/
Facebook-https://www.facebook.com/pwcc38/

